How ChatGPT Actually Searches the Web: What 1,000 Prompts Reveal About the Biggest SEO Opportunity in Years
Here's the good news that most SEO professionals are missing: ChatGPT's web search behavior is remarkably predictable. And if you understand the patterns, you can position your content to get cited in AI-generated answers with a level of precision that traditional SEO never offered.
We analyzed 994 prompts across 10 industries and 10 intent categories to map exactly when ChatGPT triggers a web search, how it reformulates queries, and what determines which pages get cited. The results reveal a massive opportunity — especially for teams using automated content generation to move at the speed AI search demands.
Here's everything we found, and why this might be the best time in a decade to rethink your content strategy.
AI Search Is More Predictable Than Google Ever Was
Traditional SEO has always been a guessing game. Google's algorithm uses hundreds of ranking factors, many of them opaque, and what works today might not work after the next core update. You're optimizing for a black box.
AI search is different. ChatGPT follows clear, observable patterns when it decides to search the web — and those patterns map directly to content you can create. There's no mystery about what triggers a search, how the query gets formatted, or what kind of content gets cited. It's all right there in the data.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total prompts analyzed | 994 |
| Prompts that triggered web searches | 196 (19.7%) |
| Average searches per prompt | 0.45 |
| Total search queries observed | 448 |
| Average citations per response | 1.79 |
Yes, ChatGPT only searches the web about 20% of the time. But that 20% represents the highest-intent, highest-value queries — comparisons, pricing research, local services, current trends. These are exactly the queries where a cited source drives real business outcomes. And unlike traditional search where you're one of ten blue links, an AI citation carries implicit endorsement. You're not just ranking — you're being recommended.
The Queries That Trigger Searches Are the Ones That Matter Most
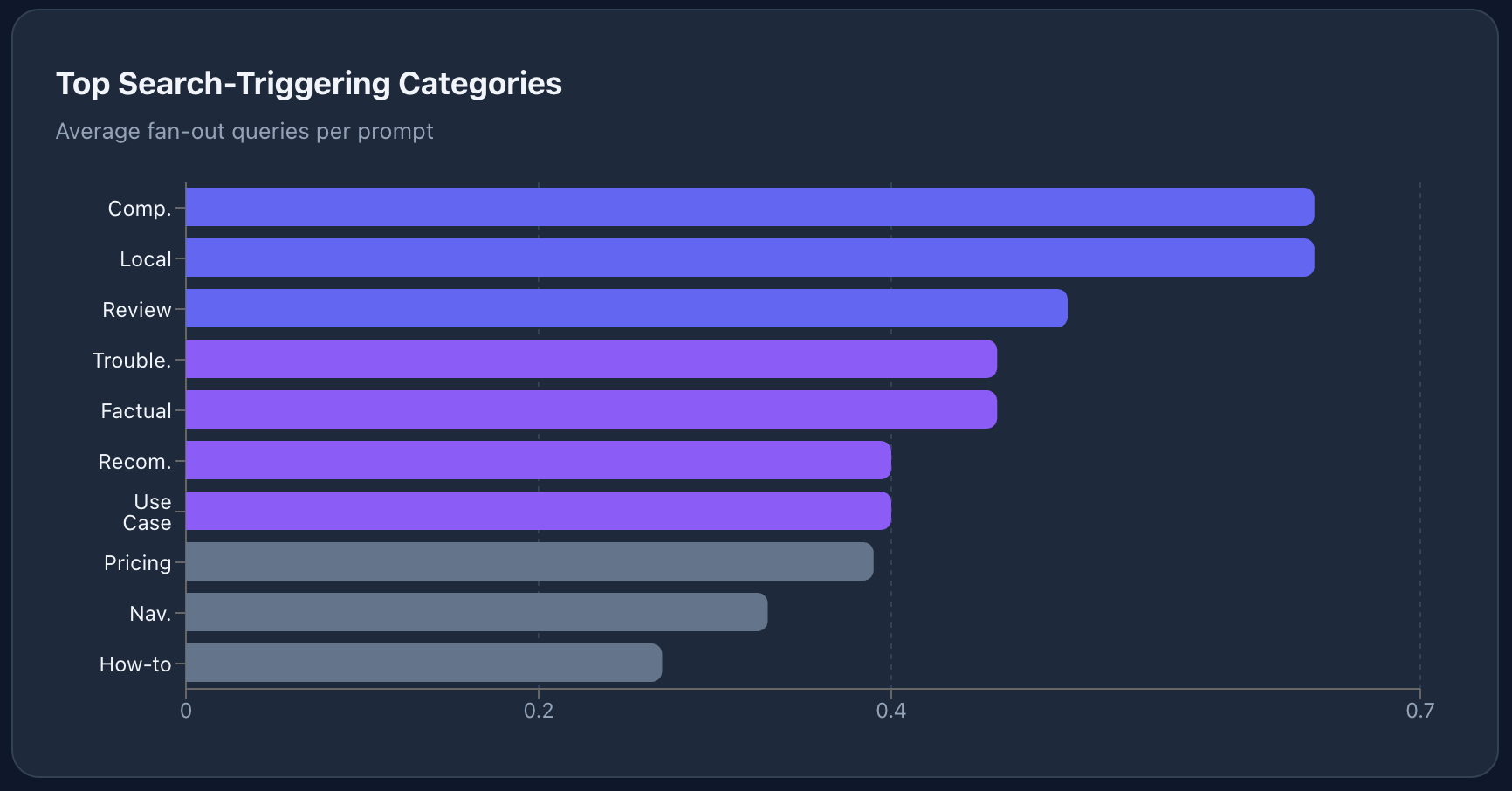
When you look at which prompt categories trigger the most searches, you'll notice something: they map almost perfectly to buying intent.
| Category | Avg Searches Per Prompt | % That Triggered Search | Avg Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | 0.64 | 23.4% | 1.82 |
| Local/Personal | 0.64 | 16.5% | 2.59 |
| Opinion/Review | 0.50 | 25.0% | 1.79 |
| Troubleshooting | 0.46 | 21.0% | 2.01 |
| Factual | 0.46 | 22.2% | 1.66 |
| Recommendation | 0.40 | 20.2% | 1.67 |
| Use Case | 0.40 | 19.0% | 1.67 |
| Cost/Pricing | 0.39 | 19.3% | 2.33 |
| Navigational | 0.33 | 16.7% | 0.93 |
| How-to | 0.27 | 13.4% | 1.46 |
Comparison, pricing, reviews, and local queries — these are the categories where people are actively evaluating options and making decisions. And these are precisely the categories where ChatGPT reaches out to the web for fresh data. The AI is essentially telling you: "These are the queries where I need your help."
Even better, the citation patterns reveal a winner-takes-all dynamic in several categories. Cost/Pricing queries generate 2.33 citations per response from only 0.39 searches — meaning ChatGPT finds one great pricing page and cites it heavily. If that page is yours, you own the category.
Local queries tell a similar story from the opposite direction: 2.59 citations per response means the AI is aggregating from multiple local sources. Every well-optimized local page has a shot at being included.
Why This Is Fundamentally Different From Traditional SEO
In traditional SEO, you optimize a page, publish it, and hope Google's crawler indexes it favorably based on hundreds of opaque signals. The feedback loop is slow, the ranking factors are hidden, and a single algorithm update can wipe out months of work.
AI search flips this model on its head in three important ways:
1. The query templates are visible. ChatGPT doesn't use your exact question as a search query. It reformulates it into predictable templates — and we can see exactly what those templates look like. When someone asks "Is Duolingo any good?", ChatGPT searches for "Duolingo review user satisfaction and educational value." That's not a mystery. That's a content brief.
2. The triggers are categorical, not algorithmic. Whether ChatGPT searches depends primarily on the type of question, not on hundreds of weighted signals. Comparison queries trigger searches. How-to queries usually don't. This is a simple, actionable framework — not a 200-factor ranking algorithm.
3. Freshness is a first-class signal. ChatGPT appends the current year to any query with recency signals. Ask about "best tools" or "latest trends" and it searches for "best tools 2026." This means recently published, frequently updated content has a structural advantage that compounds over time.
This last point is where the opportunity gets really interesting — and where automated content generation becomes not just useful, but essential.
The Speed Problem: Why Manual Content Creation Can't Keep Up
Here's the challenge with AI search optimization: the content needs to be dynamic.
Our industry data shows just how much search behavior varies by sector:
| Industry | Avg Searches Per Prompt | % That Triggered Search | Avg Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fintech | 0.60 | 27.6% | 2.42 |
| Cybersecurity | 0.59 | 22.0% | 1.95 |
| Real Estate | 0.55 | 23.6% | 2.24 |
| Marketing | 0.49 | 24.7% | 2.09 |
| SaaS | 0.46 | 20.4% | 2.01 |
| Education | 0.46 | 18.6% | 1.67 |
| Ecommerce | 0.36 | 16.8% | 1.29 |
| AI/ML | 0.35 | 16.3% | 1.52 |
| Healthcare | 0.32 | 12.9% | 1.35 |
| Fitness | 0.32 | 13.8% | 1.27 |
In fintech, more than one in four prompts trigger a search. Cybersecurity and real estate aren't far behind. These industries move fast, and ChatGPT knows it — so it reaches for fresh sources constantly.
Now think about what it takes to stay cited in these categories. You need comparison pages for every relevant product pair, updated with current pricing and features. You need review content that reflects recent user sentiment. You need local service pages with geographic specificity. And all of it needs to be year-stamped and refreshed regularly.
That's not a content calendar. That's a content engine. And this is exactly where automated content generation platforms like Cakewalk become a strategic advantage. When the AI is searching for "Stripe vs Braintree comparison features 2026," you need that page to exist, be current, and match the query template. Doing that manually across hundreds of product combinations and geographic variations simply doesn't scale.
How ChatGPT Reformulates Queries (And How to Match Them)
This is the most tactically valuable section of our research. ChatGPT doesn't pass your question to a search engine verbatim. It translates natural language into keyword-optimized queries using consistent templates — and those templates are your content blueprint.
Comparison Queries
| User Prompt | ChatGPT's Search Query |
|---|---|
| "Compare Asana vs Coda for team collaboration" | "Asana vs Coda for team collaboration comparison features Asana Coda" |
| "How does Semrush compare to Ahrefs in terms of keyword research?" | "Semrush vs Ahrefs keyword research comparison" |
Template: [Product A] vs [Product B] + [context] + comparison + [features/differences]
What to build: Structured comparison pages with the "vs" framing in the H1, side-by-side feature tables, and explicit strengths/weaknesses sections. Tools like Cakewalk can generate these at scale — which matters when you're covering dozens or hundreds of product pairs in a category.
Opinion/Review Queries
| User Prompt | ChatGPT's Search Query |
|---|---|
| "Is Duolingo any good?" | "Duolingo review user satisfaction and educational value Duolingo" |
| "What do people think about Mailchimp?" | "Mailchimp reviews what do people think about Mailchimp user opinions reviews pros cons" |
| "Pros and cons of Semrush" | "Semrush pros and cons SEO tool Semrush review advantages disadvantages" |
Template: [Product] + review/reviews + pros cons + [user opinions/satisfaction]
What to build: Review pages with explicit "Pros" and "Cons" sections, user sentiment summaries, and clear verdict language.
Factual/Statistical Queries
| User Prompt | ChatGPT's Search Query |
|---|---|
| "What percentage of B2B software companies use CRM software?" | "percentage of B2B software companies that use CRM software" |
| "How big is the artificial intelligence market in 2026?" | "size of artificial intelligence market 2026 market size AI 2026" |
Template: [Topic] + [metric] + [year/scope]
What to build: Data-rich resource pages with clear statistics, cited sources, and current year references.
Local/Personal Queries
| User Prompt | ChatGPT's Search Query |
|---|---|
| "Where can I find mortgage broker in Miami?" | "mortgage brokers in Miami FL" |
| "Best software consultant near me" | "software consultant near West Pasco WA USA" |
Template: [Service] + in/near [Location] + [best/top-rated/firms]
What to build: Location-specific landing pages with city, state, and regional keywords. This is another category where automated generation shines — creating variations for every service area you cover.
Cost/Pricing Queries
| User Prompt | ChatGPT's Search Query |
|---|---|
| "Free alternatives to Redfin" | "Free alternatives to Redfin real estate sites like Redfin" |
| "Is BigCommerce worth the price?" | "Is BigCommerce worth the price review BigCommerce cost pros cons" |
Template: [Product] + pricing/alternatives/worth the price + [review/comparison]
What to build: Comprehensive pricing pages with current data, value assessments, and alternative comparisons.
The Modifiers That Matter
Across every category, ChatGPT appends specific modifiers to improve search quality. These are the exact terms your content should include:
| Modifier Type | Terms to Include |
|---|---|
| Review/Sentiment | "reviews," "pros and cons," "advantages disadvantages," "user feedback" |
| Comparison | "vs," "comparison," "differences," "alternatives," "competitors" |
| Quality | "best," "top," "top-rated," "recommended" |
| Instructional | "how to," "setup," "guide," "steps," "fix," "troubleshooting" |
| Depth | "examples," "case studies," "best practices," "statistics," "trends" |
| Scope | "for small businesses," "for [specific use case]" |
A critical finding: ChatGPT never appends "Reddit" or any specific forum name. Despite the popular strategy of gaming Reddit for SEO visibility, the AI uses generic quality modifiers. This means first-party content with review language outperforms Reddit threads for AI citations.
The Year-Stamping Pattern: Freshness as a Ranking Signal
ChatGPT appends the current year to queries whenever recency matters — and the triggers are clear:
| Trigger | Example Prompt | Search Query |
|---|---|---|
| Explicit year in prompt | "Top 5 mortgage calculator tools in 2026" | "top mortgage calculator tools 2026" |
| "Latest" or "current" implied | "Latest trends in real estate" | "latest trends in real estate 2026" |
| "Best" or "top" with recency context | "Shopify alternatives" | "Shopify alternatives ecommerce platforms 2026" |
| Statistical/market data | "How big is the AI market?" | "size of artificial intelligence market 2026" |
Static facts ("Who founded Hugging Face?"), general how-tos, and troubleshooting queries don't get year-stamped. But anything involving "best," "top," "trends," comparisons, or market data does.
This creates a rolling content freshness requirement that's tailor-made for automated workflows. Every January, your "Best X tools in 2025" pages become invisible to AI search. Platforms like Cakewalk can programmatically update year references, pricing data, and feature comparisons — keeping your content in the citation window without manual rewrites.
Fan-Out Decomposition: How AI Breaks Down Complex Questions
When ChatGPT decides a question needs multiple searches, it uses structured decomposition to cover different angles. This is where the AI generates the most value for users — and the most opportunity for content creators.
Strategy 1: Broad → Specific
Prompt: "Compare Zocdoc vs Cerner for hospitals"
Strategy 2: Synonym Variation
| Query # | Search Query | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | "Zocdoc vs Cerner for hospitals what are differences..." | Direct comparison |
| 2 | "Zocdoc Cerner comparison healthcare scheduling EHR..." | Feature-level detail |
| 3 | "Cerner healthcare IT what is Cerner for hospitals..." | Product background |
| 4 | "overview Cerner EHR hospital software features..." | Deep product dive |
Prompt: "Penetration tester recommendations in Tel Aviv"
Strategy 3: Problem → Solution
None
| Query # | Search Query | Approach |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | "penetration tester recommendations Tel Aviv..." | Standard phrasing |
| 2 | "best penetration testing firms or consultants in Tel Aviv..." | Alternative framing |
| 3 | "cybersecurity penetration testing services" | Broadened scope |
| 4 | "cybersecurity penetration testing services Tel Aviv Israel Madsec..." | Includes known companies |
| 5 | "חברות MSSP תל אביב שירותי אבטחה מנוהלים..." | Hebrew language variant |
None
Prompt: "How to fix failed payouts in Plaid"
| Query # | Search Query | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | "How to fix failed payouts in Plaid payouts failed Plaid" | Problem restatement |
| 2 | "Plaid failed payouts resolution troubleshooting..." | Solution-focused |
| 3 | "Plaid payouts API how to troubleshoot..." | Technical docs |
| 4 | "Plaid developer docs failed payouts or transfers..." | Official docs |
The content implication is clear: comprehensive hub pages that address multiple facets of a topic can satisfy several queries from a single fan-out event. A page that covers the overview, the feature comparison, and the practical use cases captures three or four AI searches instead of one.
This is another area where automated content generation adds significant leverage. Building out hub pages that systematically cover broad overview → specific features → comparisons → use cases is a repeatable structure that tools can produce consistently across your entire content library.
7 Rules for Winning AI Search Citations
Based on our analysis, here's a practical framework for getting your content cited by AI assistants.
Rule 1: Build "X vs Y" Comparison Pages at Scale
Comparison queries trigger the highest search rate (0.64 per prompt). Structure pages with the "vs" framing in the H1, feature comparison tables, and explicit pros/cons sections. The key word here is scale — in any competitive category, there are dozens of product pairs worth comparing. Automated tools like Cakewalk make it feasible to cover the full matrix rather than cherry-picking a few matchups.
Rule 2: Year-Stamp Everything Recency-Sensitive
Include the current year in titles, H1s, URLs, and meta descriptions for any content targeting "best," "top," "trends," or comparison queries. Plan for annual (or more frequent) refreshes.
Rule 3: Own the Definitive Pricing Page
Cost/Pricing content gets cited 2.33 times per response from minimal searches. Create the single most comprehensive pricing comparison in your niche with current data, clear tables, and frank value assessments.
Rule 4: Match AI's Exact Modifier Language
Use the specific phrases ChatGPT searches for: "pros and cons," "reviews," "alternatives," "how to," "step-by-step guide," "best [type] for [use case]." These aren't just SEO keywords — they're the literal search terms the AI generates.
Rule 5: Structure Content for Multi-Query Fan-Out
Organize pages to satisfy multiple parallel queries: broad overview section, specific feature breakdowns, practical examples, and comparison to alternatives — all on a single URL.
Rule 6: Create Location-Specific Pages for Every Service Area
Local queries generate the highest citations per prompt (2.59). Build dedicated pages for each city and region you serve, with geographic terms in titles, headers, and body copy.
Rule 7: Match Your Update Frequency to Industry Volatility
The Case for Automated Content in an AI-First World
| Industry Tier | Search Rate | Recommended Update Cadence |
|---|---|---|
| High volatility (Fintech, Cybersecurity, Real Estate) | 22–28% | Monthly |
| Medium volatility (Marketing, SaaS, Education) | 18–25% | Quarterly |
| Low volatility (Ecommerce, AI/ML, Healthcare, Fitness) | 13–17% | Semi-annually |
If there's one overarching takeaway from this research, it's that AI search rewards content that is structured, current, comprehensive, and available at scale. These aren't characteristics of a blog post you spend two weeks crafting. They're characteristics of a content system.
Consider what it actually takes to fully optimize for AI search in a competitive category:
-
Comparison pages for every relevant product pair (potentially hundreds)
-
Review content updated with current user sentiment
-
Pricing pages refreshed with current data
-
Local landing pages for every service area
-
Year-stamped content updated at least annually
-
Hub pages covering multiple facets of complex topics
This is a volume and velocity challenge. The query templates are known. The modifier patterns are documented. The content structures are repeatable. What's needed is the ability to generate, publish, and maintain this content at a pace that matches how frequently the AI checks for fresh sources.
That's why platforms built for automated content generation — like Cakewalk — are particularly well-positioned for the AI search era. When you know the exact template ChatGPT uses to search for comparison content, you can systematically generate pages that match it. When you know the year-stamping pattern, you can programmatically keep content current. When you know local queries generate the most citations, you can spin up location-specific variations across your entire service footprint.
Traditional SEO rewarded patience and craft. AI search optimization rewards structure and speed. The companies that build content engines — not content calendars — will capture a disproportionate share of AI citations.
The Opportunity Is Now
AI search is still in its early innings. Most content creators haven't studied these patterns. Most SEO strategies haven't adapted to a world where the "search engine" reformulates your query, decomposes it into multiple searches, and cites the best sources it finds.
That asymmetry is the opportunity. The patterns are documented. The templates are visible. The triggers are categorical and predictable. The tools to generate optimized content at scale already exist.
The question isn't whether AI search optimization works. The data shows it does — clearly and predictably. The question is whether you'll build for it before your competitors do.
This research analyzed 994 prompts across 10 industries and 10 intent categories using the DataForSEO ChatGPT scraper API (gpt-4o). The full raw dataset is available on request.
Read Next
Best Companies for AI-First Content Strategies in 2026
The best companies for AI-first content strategies in 2026 include specialist agencies, consulting firms, and AI-native platforms that design programs around automation, AEO, and rigorous fact-checking. Buyers should assess partners on strategic depth, technology stack, ability to scale content, and how they measure AI citations alongside traditional SEO metrics.
Best Alternatives to Frase in 2026 for AI Content
While Frase is a popular AI content tool, alternatives in 2026 offer stronger SEO data, autonomous workflows, or integrated answer engine optimization. This guide compares top platforms to help you choose the best fit.
Fully Automated AEO and Content Agents: Top Platforms 2026
Fully automated AEO and content agents combine AI research, drafting, optimization, approvals, and publishing into one self-learning system. In 2026, only a handful of platforms deliver end-to-end automation, replacing manual SEO tasks while improving accuracy and speed to AI citations.